Good security programs consist of people, processes, and technology. LeastTrust IT will never try to sell you a technology tool without explaining its role in your business and in supporting specific security controls tied to global standards. Tools enforce policies and procedures. Without proper configuration and human intent, tools largely get under-utilized. Cybersecurity is continuous journey of managing an organization's largest risks and investing in people, processes, and technology that can reduce those risks. Budget and efficiency is critical to effective risk buy down
Industry leading standards such as GLBA, SOC2, SEC, NIST, CIS, ISO27001, and HIPAA drive our dedicated controls (specific defenses and strategies)
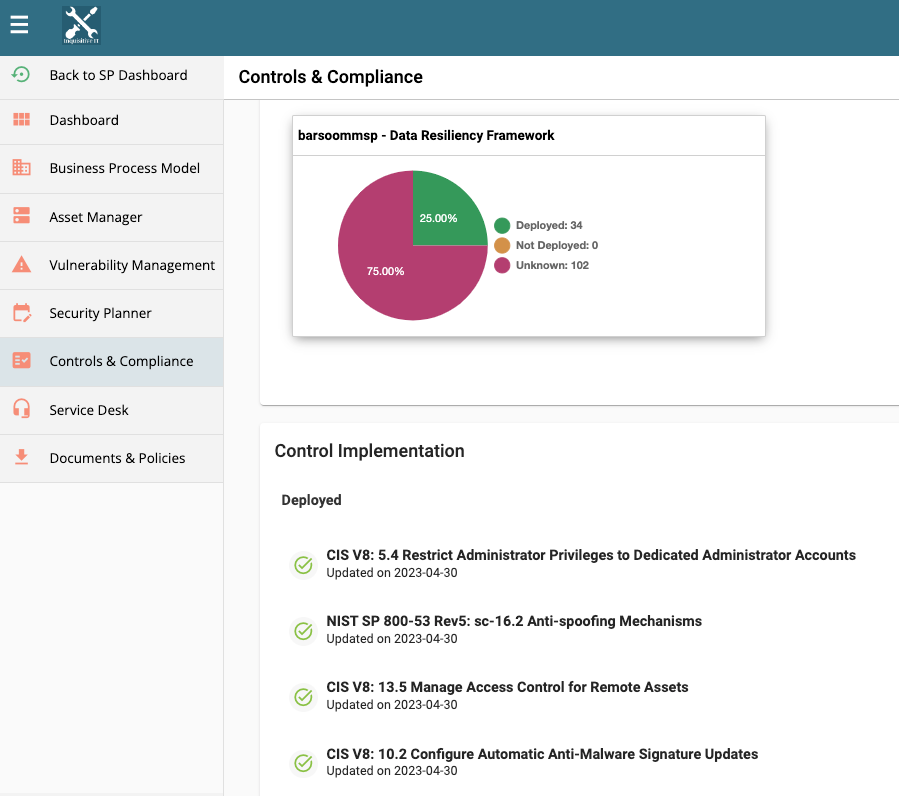
LeastTrust IT reviews and documents every control our customers implement (and the dates others will be achieved) so their stakeholders and 3rd parties have transparency when needed. This is called a SSP (System Security Plan) or POAM (Plan Of Actions and Milestones) or WISP (Written Information Security Plan)
Cybersecurity is a collaborative effort between IT providers and users. LeastTrust IT needs to know many things about your organization, systems, processes, people, roles, data types, and policies in order to better protect and retain its long term enterprise value. Culture & security awareness needs to be empowered by leadership. Our VCISO will meet with your team to build a risk registry including: business risks, IT risks, relative ranking of risks, causes of risks, risks requiring additional analysis, watchlist of low-priority risks, and risk treatment plans
Below is a list of just a sample of the controls we deploy across each IT environment we manage. Click Roadmaps to learn more about how we can secure your team.
Sample of CIS (the Center for Internet Security) Controls – The LeastTrust IT playbook to protect all organizations
1. Inventory management of Software, Hardware, Data, and 3rd party (including SaaS usage). “If you dont know what you are protecting, you can’t secure it”
2. Businesses processes, data flows, leadership and escalation points. By understanding critical IT system and data flows and how an organization uses them, together we can better architect a cybersecurity program.
3. Data access controls to critically important or sensitive data. Zero/Least Trust Architecture (ZTA) strategy to creating controlled and silo’d data access to minimize data exposure and increase resilience. Instead of giving all access to all employees, ZTA aims to start with “what is the minimum access needed per each employee to each data asset or system?” If one user is compromised, damages and and rebuild are minimized.
4. “Allowlists” and “do not allowlists” of software and services accessible by employees. By limiting software, add-ins, plugins, and scripts to what is necessary for business greatly reduces the attack surface area (What actually needs to be protected, maintained, and monitored)
5. Daily vulnerability scanning and management. Scanning for vulnerabilities with agent based scanners is critical to removing entry points for attackers.
6. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) – MFA is a modern authentication strategy of requiring more than form of authentication (for example password then phone or biometric auth) to make it more difficult for hackers or adversaries to access an organizations systems. Phishing resistant MFA is an enhanced authentication tools that we frequently deploy (PassKeys, YubiKeys)
7. Complex passwords and the use of a password manager. By creating unique complex passwords for systems and using a password manager prevents (Brute force attacks – trying simple passwords over and over by machines).. Password managers should make it easier for employees to access systems without remembering each unique & complex password.
8. Apply regular patching updates to machines and software. This is a critical aspect of vulnerability management and regularly removing new vulnerabilities.
9. Collect logs from as many sources as possible, but most important are access logs, failed login attempts, new devices on the network, etc. Logs are critical after an attack to understand and re-engineer defenses to prevent a similar attack in the future.
10. Disable removable drives (USB) and authorize one or few cloud supported data sharing services (Google Drive is our favorite given its integration with Google Workspaces).. Limiting access and support for data sharing medium will make it easier to control data sharing and review access logs.
11. Enable data “at rest” and “in transit” encryption. Encryption secures data while being stored and sent by scrambling data so that a key is necessary to read & access the data.
12. Enable and authorize one specific internet browser for commercial use. By controlling browser and its associated plug-ins will limit data leakage, limit software allowlist, and un-authorized shadow IT or data access. (Chrome & Google authentication make this manageable)
13. Enable mobile management features to allow mobile organizational email access, contacts, and calendar. (We use google device management to accomplish this or skip BYOD with Yubikeys)
14. Conduct regular employee training and cyber awareness on controls, data access, and phishing.
14. Establish process and policies for provisioning new users and revoking exiting employees. Enable log out of devices when necessary, Enable Screen Lock, Enable Remote Wipe, Disable Toasts
15. Establish an incident response policy for a step by step playbook and escalation chain in times of a incident.
16. Rehearse and simulate attacks to test and improve incident response, employee training, and identifying areas of possible improvement
17. Enable Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR). EDR is a critical sensor and alarm system to identify unusual activity, unauthorized access, and quarantine systems or access.
18. Enable a VPN (Virtual Private Network) for remote access. VPNs are critical to protecting devices when used outside the core network and using a public wifi network.
Security & Risk Collaboration Dashboard
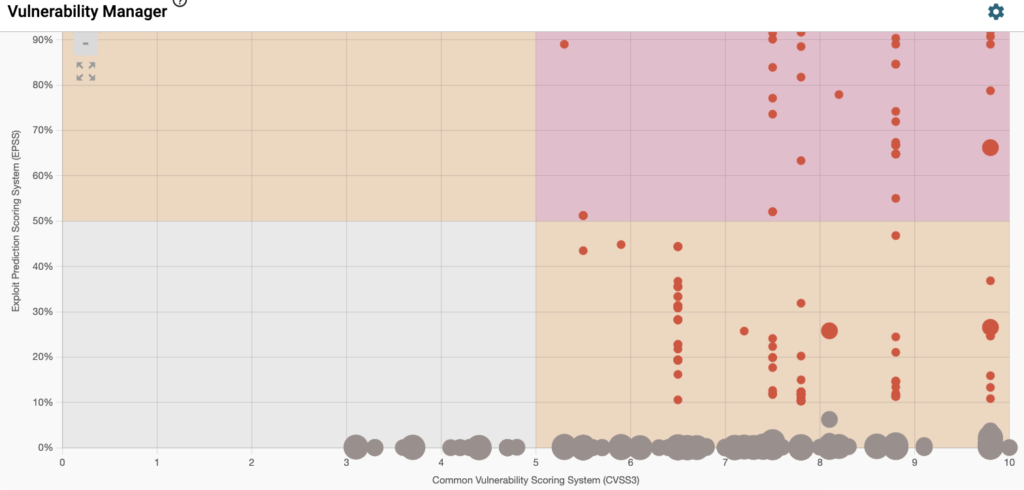
Vulnerability Management (Using AI Based prioritization of the most dangerous vulnerabilities)
Learn More
Nationwide Coverage
Our Team is located across the United States and can respond to your needs virtually in real time or be on location in hours.